The pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on high-quality water for the production of drugs, formulations, and other healthcare products. Among various water types, purified water holds a significant position. Its generation and maintenance are crucial, as it directly impacts the quality and safety of the final product. This article delves into the essentials of purified water generation systems in the pharmaceutical industry, their processes, and their role in ensuring compliance with stringent quality standards.
Importance of Purified Water in Pharmaceuticals
Purified water is primarily used for cleaning equipment, as an ingredient in non-sterile products, and as feedwater for generating Water for Injection (WFI) or pure steam. The absence of contaminants such as dissolved salts, organic matter, and microorganisms is critical in maintaining the integrity of pharmaceutical products. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopeia (EP) have established strict standards for purified water, emphasizing its chemical and microbiological purity.
Key Components of a Purified Water Generation System
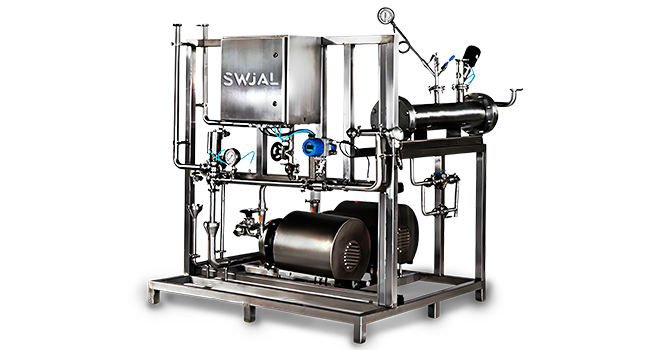
A pharmaceutical-grade purified water generation system consists of several advanced components designed to ensure consistent water quality. These include:
-
Pre-Treatment Units
- Filtration Systems: Remove suspended solids and reduce turbidity.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Eliminate chlorine and organic compounds.
- Softening Units: Remove hardness-causing ions like calcium and magnesium.
-
Primary Treatment Systems
- Reverse Osmosis (RO): Removes up to 99% of dissolved salts, organics, and microorganisms through a semipermeable membrane.
- Electrodeionization (EDI): Utilizes ion exchange membranes and electricity to polish the water further, achieving ultrapure levels.
-
Post-Treatment Units
- Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection: Inactivates microorganisms.
- Micron Filtration: Removes fine particulates before water storage or distribution.
-
Storage and Distribution System
Proper storage tanks and distribution systems are essential to maintaining water quality. These systems are designed with a recirculation loop to prevent microbial growth and stagnation.
The Purification Process
The water purification process in the pharmaceutical industry typically involves multiple stages:
- Raw Water Pre-Treatment: Removes larger particles and contaminants that can damage the subsequent systems.
- Primary Treatment: Reverse Osmosis is used to filter out smaller impurities, ensuring high efficiency.
- Polishing Stage: Electrodeionization or distillation processes are employed to achieve pharmaceutical-grade purity.
- Sterilization and Storage: UV systems and heat sanitization methods keep the purified water free from microbial contamination.
Automation and Monitoring
Modern purified water generation systems are equipped with advanced automation and monitoring features. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) ensure seamless operation, while real-time monitoring of critical parameters such as conductivity, total organic carbon (TOC), and microbial count guarantees compliance with pharmacopoeial standards. Alarm systems notify operators of any deviations, enabling immediate corrective actions.
Regulatory Compliance
Pharmaceutical water systems must adhere to regulatory guidelines. Key standards include:
- USP and EP Monographs: Define the purity levels for purified water.
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice): Outlines best practices for designing and maintaining water systems.
- ISO 9001: Ensures that quality management systems are in place.
Validation is an integral part of regulatory compliance, involving installation qualification (IQ), operational qualification (OQ), and performance qualification (PQ). Regular microbiological testing, calibration, and preventive maintenance are essential for sustained compliance.
Challenges and Solutions
-
Microbial Contamination
Controlling microbial growth is one of the most significant challenges in purified water systems. Continuous recirculation, UV disinfection, and periodic sanitization address this issue effectively. -
Scaling and Fouling
Pre-treatment methods like softening and antiscalant dosing help prevent scaling in RO membranes, while regular cleaning-in-place (CIP) reduces fouling. -
Energy Efficiency
Modern systems focus on energy-efficient components such as high-recovery RO membranes and advanced energy recovery devices, reducing operational costs.
Future Trends
The pharmaceutical industry is witnessing advancements in water purification technologies, including hybrid systems combining multiple purification methods, IoT-enabled monitoring, and greener, more sustainable systems. These innovations aim to enhance water quality while minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion
Purified water generation systems form the backbone of pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring the consistent supply of high-quality water essential for producing safe and effective medicines. From pre-treatment to advanced polishing, these systems are designed to meet stringent industry standards. Regular validation, automation, and preventive maintenance further ensure reliability and compliance.
Swjal Process is a leading Pharmaceutical Grade Water Generation and Distribution Plant Manufacturer in India.
